Find an Orphan-Enriched RNA-Seq dataset from NCBI-SRA
See the detailed scripts here .
Notes:
This step is optional, and applies to species with >40 available SRA RNA-Seq runs. It is designed to provide a diverse dataset, rich in representation of all genes including orphan genes.
If the species you are annotating has fewer than ~40 SRA RNA-Seq runs, download it all and go on to one of the ab initio prediction methods.
If you are relying solely on RNA-Seq data that you generate yourself, *maximize* representation of genes by including diverse conditions like reproductive tissues, biotic and abiotic stresses, and a variety of other tissue and organ types.
Select RNA-Seq SRR ID from NCBI-SRA website for your desired species:
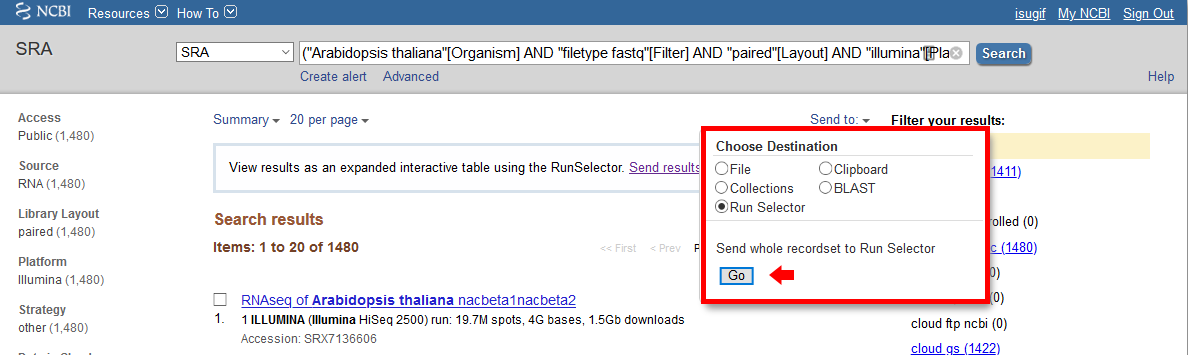
Go to NCBI SRA page and search with “SRA Advanced Search Builder”. This allows you to build a query and select the Runs that satisfy certain requirements. For example:
1("Arabidopsis thaliana"[Organism] AND
2 "filetype fastq"[Filter] AND
3 "paired"[Layout] AND
4 "illumina"[Platform] AND
5 "transcriptomic"[Source])
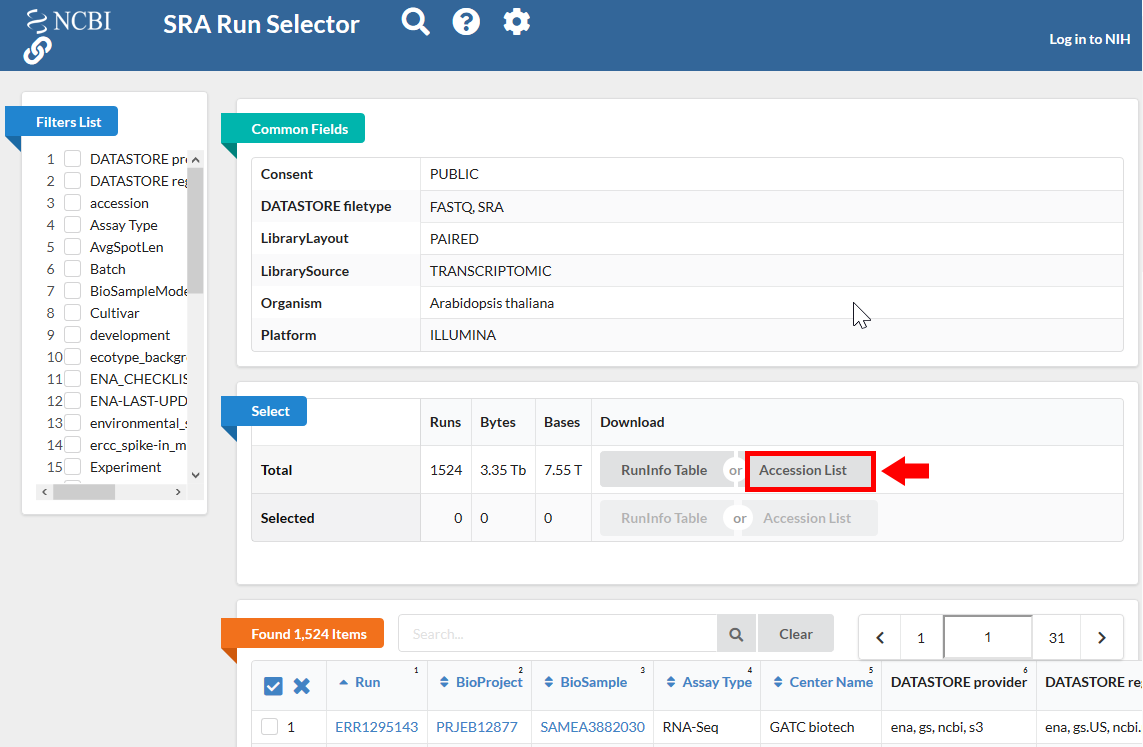
Then export the results to “Run Selector” as follows:
Clicking the “Accession List” allows you to download all the SRR IDs in a text file format.
Download RNA-Seq raw reads:
1 while read line; do
2 ./01_runSRAdownload.sh ${line};
3 done < SRR_Acc_List.txt
Note: depending on how much data you find, this can take a lot of time and resources (disk usage). You may need to narrow down and select only a subset of total SRA runs. Another way to choose datasets with maximal orphan representation is to select SRRs most likely to be diverse (eg: stress response, flowering tissue, or SRRs with very deep coverage).
Download the CDS sequences for the organism you are annotating, and build transcriptome for kallisto index:
1wget https://www.arabidopsis.org/download_files/Genes/Araport11_genome_release/Araport11_blastsets/Araport11_genes.201606.cds.fasta.gz
2gunzip Araport11_genes.201606.cds.fasta.gz
3kallisto index -i ARAPORT11cds Araport11_genes.201606.cds.fasta
For each SRR ID, run the Kallisto qualitification:
1while read line; do
2 02_runKallisto.sh ARAPORT11cds ${line};
3done < SRR_Acc_List.txt
Merge the tsv files containing counts and TPM:
103_joinr.sh *.tsv >> kallisto_out_tair10.txt
Note: For every SRR id, the file contains 3 columns, effective length , estimated counts and transcript per million .
Run phylostratr to infer phylostrata of genes, and identify orphan genes:
Build a phylogenic tree for your species, and download proteins sequences for target species:
1./04_runPhylostratRa.RRun Blast to compare query proteins and target proteins:
1while read line; do 2# 3702 is taxid for our focal species A.thaliana. 3# You can replace your own protein sequences for your focal species if protein downloaded from uniprot is not your desired version. 4 05_runBLASTp.sh ${line} 3702.faa; 5done < uniprot_list.txt
Process Blast output and stratify phylostrata level for each query gene:
1./06_runPhylostratRb.RNote: Phylostratr will run protein blast automatically if it doesn’t detect blast database and output files in working directory, so you can skip step2 to obtain blast output. However, it may takes a long time depend on the number of species and the size of your query genes. You can also use
strata_diamondinstead ofstratain06_runPhylostratRb.R, it will use Diamond Blast instead of Blast-plus. Diamond blast is much faster than Blast-plus, but may not sensitive as Blast-plus.
Select Orphan-rich RNA-Seq data:
Once the orphan (species-specific) genes are identified, count the total number of orphan genes expressed (>1TPM) in each SRR, rank them based on % orphan expressed. Depending on how much computational resources you have, you can select the top X number of SRRs to use them as evidence for direct inference and as training data.
Note: for Arabidopsis thaliana, we used all of the SRRs that expressed over 60% of the orphan genes (=38 SSRs).